Water Softener System Guide: How to Find the Best for Your Home

But here’s the thing. How do you find the best water softeners?
If you don’t know much about the topic, this question can become overwhelming quickly. After all, buying a softener is a significant investment, and there’s much information out there to sift through.
To simplify things, we’ve compiled everything you need to know into this comprehensive guide. The main topics covered include:
- Understanding Hard Water vs. Soft Water
- The Problems Hard Water Causes
- The Problems with Radium and Barium
- The Many Benefits of a Water Softener System
- How Water Softener Systems Work
- The Different Types of Water Softeners
- Salt-Based Water Softeners vs. Salt-Free Water Conditioners
- An Overview of Popular Water Softener Brands
- How to Find the Right Size Water Softener
- Tips for Choosing the Best Water Softener
- The Importance of Professional Water Softener Installation
- Water Softener Maintenance Best Practices
- Water Softener FAQs
We hope this guide helps you find the best water softener for your home.
Before we begin, we should also mention that we sell and professionally install water softeners throughout Northern Illinois and Southeast Florida. You can visit our service page to learn more about all that we offer.
Now that that’s out of the way, let’s begin the guide!
Understanding Hard Water vs. Soft Water
The most basic function of a water softener system is to turn hard water into soft water. However, not everyone knows the difference between these two types of water and why soft water is better.
Softening your water has many benefits. To understand those benefits, we must first understand the difference between hard and soft water.
As we will see, this difference has to do with the mineral content of the water.
Hard Water Contains Excess Minerals
Let’s start by defining hard water. To do this, we must first examine where the water in your home comes from and how that affects its composition.
The water you use every day once flowed through the earth before it came into your home.
Water is naturally adhesive, meaning it sticks to the substances it interacts with. So, as water flows over the rocks that make up the earth’s crust, it collects little bits of these minerals and carries them along with it.
As a result, the minerals in the ground in your region are the minerals you will likely find in your water.
Hard water has collected a high amount of minerals like calcium and magnesium as it flows through the earth. The water can also sometimes contain minerals like iron, manganese and sulfur.
Because we define hard water by how many minerals it contains, not all water is equally hard.
We determine how hard water is by how many grains per gallon (gpg) it contains. Water must contain at least one grain per gallon to be considered hard. The rest of the scale looks like this:
- Slightly hard: 1-3.5 gpg (17-60 mg/L)
- Moderately hard: 3.5-7 gpg (60-120 mg/L)
- Hard: 7-10.5 gpg (120-180 mg/L)
- Very Hard: over 10.5 gpg (over 180 mg/L)
Most homes in the United States have at least slightly hard water. However, many areas have hard to very hard water, as is illustrated by the white and red regions on this map.
At Angel Water, we serve the Northern Illinois and Southeast Florida regions. Both areas have water that is considered very hard.
As we will see, this high mineral count can create many problems for homeowners in these sections of the country.
Soft Water Contains Very Few Minerals
Soft water contains less than one gpg of minerals like calcium and magnesium. Note that water does not have to be completely free of these minerals to be considered soft. However, water with less than one gpg will not produce the hard water problems listed in the next section.
Still, there is such a thing as truly soft water, meaning water with 0 gpg. You’ve experienced it if you’ve ever been caught in the rain.
Rainwater is naturally soft because it falls from the sky and contains no hard water minerals. It becomes hard only after it hits the ground and starts collecting minerals.
So, soft water is natural and good for your body and home. As we will see, water softeners play a crucial role in returning water as closely as possible to its original state when it was once a tiny raindrop.
The Problems Hard Water Causes
To recap, the difference between hard and soft water is that hard water contains many minerals, and soft water doesn’t.
Now that you understand the difference, you’re probably wondering what the big deal is for water to contain a lot of calcium and magnesium. Aren’t those elements good for you? So, wouldn’t water softeners make your drinking water less healthy?
We want to answer these excellent questions upfront: Drinking hard water will not cause. In fact, calcium and magnesium are essential nutrients for a healthy diet in moderation. They can only make you sick if you consume way too much of them, but that’s true for just about anything.
However, just because hard water is generally safe to drink does not mean it’s something you want in your home.
As we will see below, hard water can be more difficult than it’s worth when bathing, cleaning, and accomplishing other household tasks.
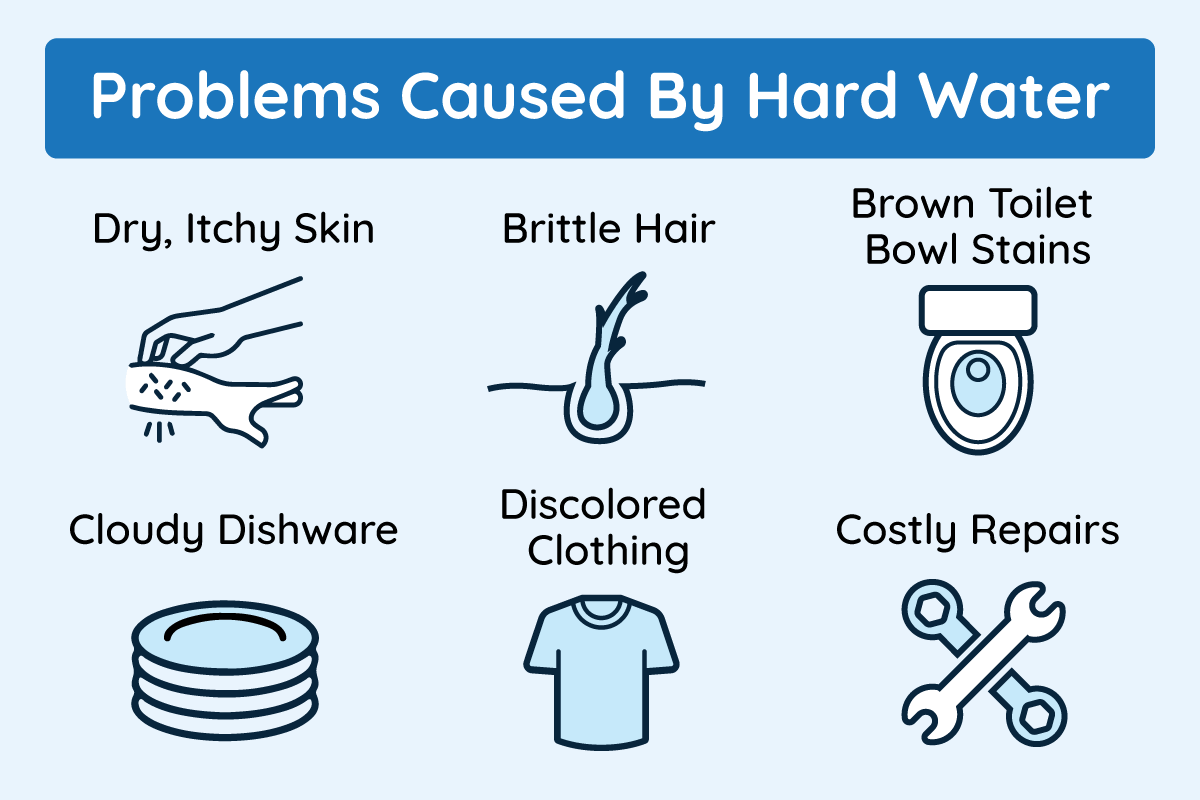
Let’s take a quick look at some of the issues hard water can cause:
Dry, Itchy Skin
Hard water is no friend to showering and hand washing. The excess minerals mix with any soap used for washing to form a curd known as soap scum. Instead of sliding off your skin when you rinse, that scum sticks to your skin, clogging up your pores. The water also sheds excess calcium and magnesium particles, which glob onto your skin.
As you might expect, the results are not pretty.
This sticky layer of soap scum and minerals acts as a barrier between your skin and the natural oils it needs to stay moist. Your skin quickly becomes a dry, itchy desert as a result. This suffocating effect can also cause wrinkles and worsen skin diseases like eczema.
Fortunately, a water softener can intervene in this process and allow your skin to get the moisture it needs. But as long as those hard water minerals clog up the process, you and your skin will suffer.
Brittle Hair
Hard water has a similar effect when you try to wash your hair with it. For one thing, it will dry out your scalp by leaving behind mineral deposits and soap scum. But beyond this, it will also mess with your hair at a microscopic level, leaving it a brittle and frizzy mess.
Each strand of your hair is covered in tiny little scales. Washing your hair with soft water makes those scales flat so that your hair feels smooth and easy to comb. Conversely, the excess mineral count of hard water makes those scales stand up. The hair feels brittle and becomes hard to untangle and maintain.
Brown Stains in Your Toilet Bowl
Don’t snicker. We know you’ve seen this phenomenon before, perhaps even in your own home. The toilet receives regular cleaning yet still gets these unsightly brown stains that are hard to remove. This annoying problem is usually another symptom of hard water.
It happens when the water contains excessive amounts of iron or manganese, along with calcium and magnesium. The calcium minerals etch away at the toilet’s sheen, and then the iron and manganese stain those etched areas brown.
Unfortunately, traditional bathroom cleaners cannot remove these brown stains. However, the right water softener can prevent them before they happen!
Cloudy Dishware
Like how it can mess up your showers, hard water can also make washing the dishes a nightmare. Once again, the issue stems from how the excess minerals interact with your dish soap. They combine to form a soapy film that sticks to your dishes and holds in dirty water rather than rinsing off.
Because of this, your wine glasses and fine china will be covered in white splotches when they come out of the dishwasher. It’s an embarrassing problem, especially when you’re having company over.
Discolored Clothing
Equally embarrassing is how hard water can discolor and fade your laundry over time. The hard water minerals don’t mix well with the laundry soap. This volatile combination produces scummy residue that can stick to the clothing and weaken its fibers. The result is dingy duds that will have to be replaced sooner rather than later, costing you more money.
Costly Repairs
That brings us to one of the worst problems with hard water: the strain it can put on your wallet. How is hard water expensive? Let us count the ways:
- The excess calcium minerals can cause your dishwasher and water heater to break down.
- It makes your household cleaning supplies less effective, so you must buy more.
- You’ll have to use more soap and shampoo to achieve an effective lather.
- Mineral buildup can clog up your plumbing system, leading to expensive plumbing bills.
These are just a few ways hard water can make your life harder. But enough about water hardness.
Let’s shift our focus to radium and barium, two other harmful contaminants a water softener system can help with.
The Problems with Radium and Barium
Along with hard water minerals, the best water softeners can also remove some harmful pollutants from water, including radium 226/228 and barium. In this section, we’ll explain these elements, how they can get in your water and the problems they can cause.
Radium 226/228 in Drinking Water
Radium is a naturally occurring element often found in the earth’s crust. It forms from the radioactive decay of uranium and thorium, and its two most common isotopes are radium-226 and radium-228. (For this post, we will refer to them together as radium 226/228.)
The amount of radium 226/228 in a water supply will depend on the region’s geology. The areas with the highest levels of radium contamination have granite bedrock surrounding their aquifers. Because granite bedrock typically surrounds deeper aquifers, homes that get water from shallow private wells are less at risk.
Health Guidelines for Radium
At Angel Water, one of the areas we serve, the greater Chicago region, is notorious for having radium in its granite bedrock. Most of the towns and cities in this area do not have radium levels that exceed the five pCi/L limit set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Still, any amount of pollution is too much.
Furthermore, other organizations like the Environmental Working Group (EWG) have pointed out that the EPA’s limits are outdated and not strict enough to protect public health. The EWG has much more stringent limits of 0.05 pCi/L for radium-226 and 0.019 for radium-228, which are frequently exceeded throughout the Northern Illinois region. For example, the Village of Buffalo Grove, IL, has some of the highest radium levels in the country.
The Dangers of Radium Consumption
There are many good reasons for such strict limits on radium 226/228. Drinking water containing these pollutants can increase the risk of cancer, kidney disease and developmental defects in fetuses.
Plus, radium decay can lead to the formation of radon gas, which is the second most common cause of lung cancer in the country.
Since radium 226/228 is invisible, odorless and tasteless, it’s impossible to tell if it’s in your water without performing a water test.
For these reasons, investing in a water softener that filters out radium 226/228 can be worthwhile.
Barium in Drinking Water
Barium is another common naturally occurring element that some water softener systems can remove. It’s typically found in mineral deposits in the earth’s crust and can get into groundwater that way. However, barium contamination can also come from oil or natural gas drilling, copper smelting or manufacturing processes.
The EPA has set the maximum contaminant level for barium at 2,000 ppb. However, the EWG points out that this limit was set over 30 years ago and does not adequately protect human health. Their much stricter health guideline is 700 ppb, which towns like Lake Zurich, IL, have exceeded in recent years.
Consuming water containing high levels of barium can potentially lead to many health problems, including high blood pressure, heart rhythm abnormalities, swelling of the brain, muscle weakness and more.
Fortunately, as we will see, removing barium is one of the many wondrous benefits of owning a quality water softener.
The Many Benefits of Water Softeners
Enough with the bad news about everything that could be wrong with your water! It’s time to focus on the positive.
Water softener systems provide numerous benefits for your home and health. They do this by removing hard water minerals and contaminants from the water in a process called ion exchange. We will get into how that process works in the next section. For now, let’s say that the right water softeners can give you the soft, healthy water you deserve.
So, instead of having to live with the damaging effects of hard water, you can get all the following benefits and more:
- Healthier and softer skin and hair without harmful soap scum and mineral buildup
- Less money spent on soap, shampoo, dish soap, detergent and cleaning products
- Less wear and tear on water-using appliances like your coffee maker, dishwasher and water heater
- No scale accumulation or clogs in your plumbing from mineral residue
- No embarrassing spots left behind on dishware
- Clean clothes free from damage and discoloration
- Lower energy bills as water-using appliances work more efficiently
- No unsightly brown stains in the toilet, sinks or shower
- Protection from dangerous radium 226/228 and barium contamination
So, as you can see, water softeners can improve your home and health in many ways. You’ll be more comfortable in your skin, and household chores like washing the dishes, doing laundry and cleaning the bathroom will be much less stressful.
How does a water softener system accomplish all this? We’ll look at how these impressive machines work next.
How Water Softeners Work
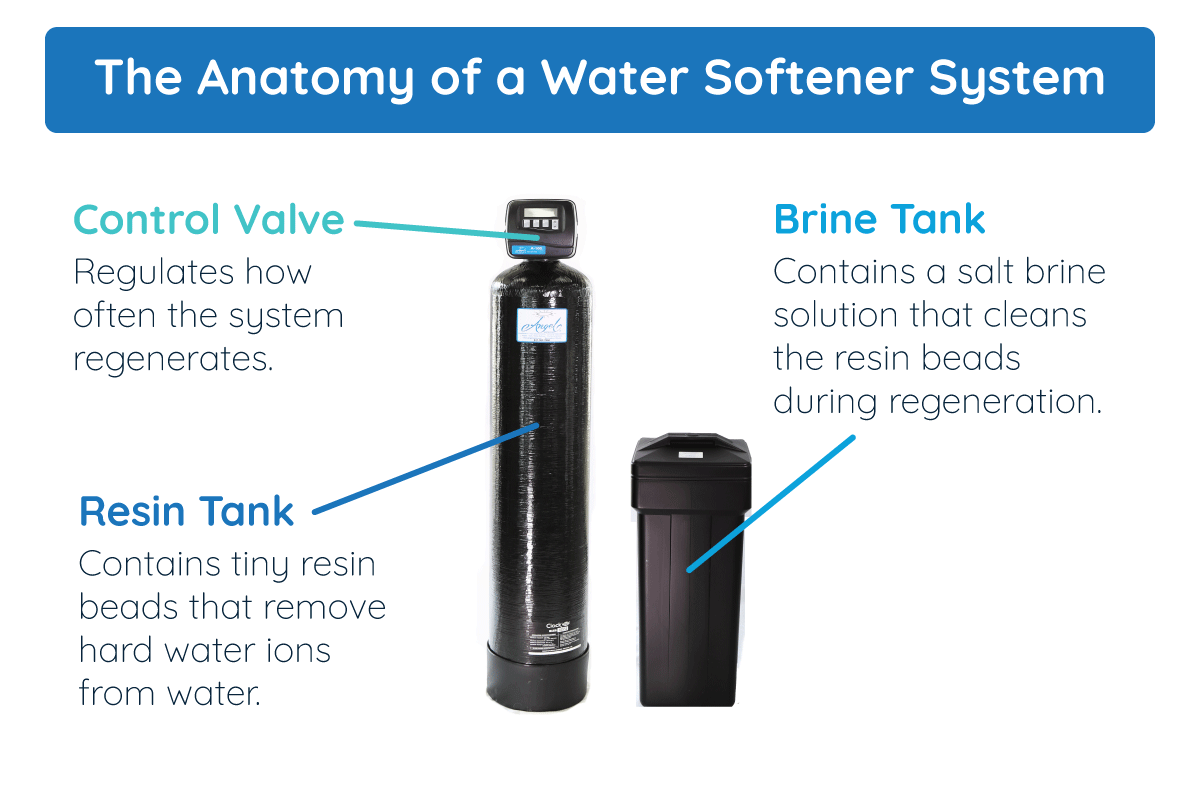
Water softeners have two main functions. The system’s primary function is to soften water before you use it in your home. Its second function is to take care of itself to keep your water soft continually.
A typical system will have two tanks to help it accomplish these tasks. The tank primarily responsible for softening the water is called the resin tank. The other tank, which helps keep the system working properly, is called the brine tank.
Let’s look at how these tanks work together to produce consistently soft water.
The Resin Tank Eliminates Hardness
The resin tank gets its name because it contains hundreds of tiny resin beads. These beads are essential in removing the hardness ions from water. They are effective at this because they have a negative charge, which attracts the positive charge of the hardness ions.
Hard water enters the resin tank through a valve at the top and flows down into the resin beads. The positively charged harness ions then leap out of the water and latch onto the negatively charged beads. Once the beads have taken all the hardness ions out of the water, the newly softened water exits the tank and flows to your plumbing system for use.
In this way, the resin beads accomplish the invaluable task of removing hardness ions from the water. But the tiny beads can only hold onto so much residue before losing effectiveness. Thankfully, the brine tank is there to help the beads keep doing their important work.
The Brine Tank Helps Clean the Resin Tank
You’ve probably seen or heard about people pouring a bag of big white salt pellets into a water softener and wondered why that’s necessary. The reason is that the brine tank needs the salt to help keep the water softener system running right.
When you pour salt into a softener, you pour it into the brine tank, which is usually the shorter of the two tanks. Often, it looks like a garbage can.
The salt mixes with water inside the tank, forming a brine solution. The solution is then periodically sucked out of the brine tank and into the resin tank to clean the hard water ions off the beads in a process known as regeneration.
What makes this brine solution effective at cleaning off the resin beads? The salt contains sodium or potassium ions that have a positive charge. So, when the solution flows over the negatively charged beads, they let go of the hardness ions to latch onto these new sodium or potassium ions. For this reason, people often refer to the water-softening process as an ion exchange process.
All of this happens during a water softener’s regeneration cycle. We’ll look at how that works next.
How the Regeneration Cycle Works
Regeneration is to clean the resin tank and prepare it to soften more water. The cycle consists of a three-phase process:
- Backwash Phase: The resin tank backwashes itself to eliminate any accumulated dirt or sediment in the tank.
- Brine Phase: The brine solution enters the resin tank and cleans the hardness ions off the resin beads.
- Rinse Phase: Water rinses the brine solution and the hardness ions down the drain.
Once the cycle is complete, the clean resin beads are ready to soften more water. The system also refills the brine tank with more water to be prepared for the next regeneration cycle.
The control valve at the top of the water softener manages how often the system regenerates. Some systems regenerate automatically after a certain amount of time has passed. More sophisticated systems monitor the amount of water used and only regenerate when the amount is about to exceed the resin beads’ softening capacity.
Water softener owners should know that most softeners can’t soften water during regeneration. So, no soft water will be available to the home for the duration of this phase. For this reason, it’s a good idea to program your softener only to regenerate when no one is using water, such as in the middle of the night.
Still, some systems have a dual-cylinder setup, regenerating only one tank at a time. Because of this, soft water is always available, even during regeneration.
The Importance of a Bypass Valve
Every water softener system should also have a bypass valve. This valve is essential because it lets you turn off the water to your softener during maintenance while keeping the water flowing to the rest of the home.
Using a bypass valve often involves turning the valve one way to open it and another way to close it. For example, EcoWater brand water softeners have two types of bypass valves: one with a lever and another with a nob that you push for bypass.
The Different Types of Water Softeners
Many types of water softeners exist, but not all provide the same benefits. Plus, some systems are much more effective than others. So, which type of water softener system is right for you?
Here are some of the most popular types of water softeners available:
- Salt-Based Water Softeners
- Salt-Free Water Conditioners
- Dual-Tank Water Softeners
- Magnetic Water Softeners
- Portable Softeners
- Showerhead Softeners
- Template Assisted Crystallization
Below, we’ll take a closer look at each of these to help you determine which makes the most sense for your situation:
Salt-Based Water Softeners
Salt-based systems are the most popular and well-known type of water softener. And there’s a good reason for their continued popularity: they work.
A salt-based water softener uses the tried-and-true ion-exchange method we described above. The resin tank softens the water, and the brine tank periodically cleans the resin.
The only burden for homeowners with salt-based systems is that they require periodic salt refills and maintenance. Still, you can hire a licensed professional to do this for you if you don’t want to lug those heavy salt bags.
We feel the long-term effectiveness of a salt-based system certainly outweighs these minor drawbacks.
Salt-Free Water Conditioners
A popular alternative to a salt-based system is a salt-free water conditioner. Note that we didn’t call this option a salt-free water softener system. This is because the term “salt-free water softener” is a misnomer.
In truth, salt-free systems don’t soften water. They condition it so it doesn’t form a scaly buildup in plumbing pipes.
As the water flows through the salt-free system, a chemical reaction crystalizes the hardness ions, effectively neutralizing their hardness. The problem is that this reaction only lasts for so long. Once the water leaves the faucet, it still contains calcium and magnesium minerals that can smudge up your dishes, stain your toilets and dry out your skin and hair. In other words, it’s still hard!
So, you should only get a salt-free system if you’re mainly concerned with preventing scale within your plumbing system. If that’s you, then you will also enjoy the fact that the system doesn’t require salt refills and takes up less space than a salt-based system.
But if you want soft water, stay away.
Dual-Tank Water Softeners
A dual-tank water softener system does the same things as a salt-based system. The only difference is that it has two resin tanks to the standard salt-based softeners. It has two tanks so that the water-softening process won’t be interrupted by regeneration. When one tank needs regeneration, the other tank can still soften the water.
Because of the extra tank, dual-tank systems tend to be more expensive than single-tank models. Yet, that extra expense may be worth it in homes that use a lot of water. It may also help households where some people work the night shift and would be inconvenienced by middle-of-the-night regeneration cycles.
Magnetic Water Conditioner
A magnetic water conditioner is a salt-free system that uses electromagnetic coils to separate hardness ions from water droplets.
The effectiveness of this system is suspect at best because, just like every other salt-free option, it doesn’t remove the hard water minerals from the water. Instead, it temporarily changes the chemical composition of the ions so that they won’t form scale in the plumbing system. The water still leaves the faucet containing calcium and magnesium minerals, which can cause hard water problems.
So, even though this option is cheaper and lower maintenance than salt-based systems, don’t go with it if you’re looking for quality. The system only prevents scale in plumbing, and it doesn’t always do the best job at that since the magnets aren’t always strong enough to crystalize all the water hardness ions.
In short, you get what you paid for with this cheap option.
Portable Water Softeners
Maybe you don’t need enough soft water to supply a whole house. In that case, a portable water softener might be the way to go. These mini salt-based systems are great for families with RVs or campers. They can supply enough soft water for a bathroom or kitchen sink and go a long time between regeneration cycles.
So, if you’re looking for a little soft water on the go, you can’t go wrong with going portable.
Showerhead Water Softeners
Perhaps the only effect of hard water that bothers you is that it dries out your skin and hair in the shower. In this case, a showerhead softener is an excellent, cost-effective option.
This mini softener is a little filter that easily fits inside a specially designed showerhead. It provides enough soft water for a few months before requiring replacement.
Template Assisted Crystallization
Template-Assisted Crystallization (TAC) is another salt-free alternative to ion-exchange systems. A TAC system uses a chemical process to change the structure of calcium and magnesium ions, preventing them from forming limescale on dishes, showerheads, plumbing pipes and more.
Once again, since this system doesn’t eliminate the calcium and magnesium in the water, it’s debatable how effective it is at eliminating hard water problems. While it seems more effective than magnetic conditioners, it still can’t guarantee that the excess minerals won’t dry out your hair and skin.
In short, the jury’s still out on the effectiveness of TAC, but it’s a lower maintenance alternative to standard salt-based systems.
Salt-Based Water Softeners vs. Salt-Free Water Conditioners
As you may have guessed, we have a favorite in the debate between salt-based and salt-free systems.
We favor salt-based water softeners because they provide more benefits than their salt-free counterparts. A salt-based system provides better soap lather, smoother skin, brighter clothing and no scale on plumbing, just to name a few. Conversely, salt-free systems can only eliminate scale from your plumbing systems. That’s it.
So, if you don’t mind refilling your brine tank with salt occasionally, you will be much better off going with a salt-based water softener. We rest our case.
An Overview of Popular Water Softeners Brands
Another important decision you must make when buying a water softener is which brand to choose. The sheer number of brands can make this a very difficult decision.
NEW! Stop Wasting Money!

Are you spending money every month on Bottled Water for your home or office? That adds up quickly and with inflation, it’s only going to cost more tomorrow.
With the NEW purAsure Counter top Reverse Osmosis System you never have to pay for another case of plastic bottles! Get yours before the price goes up and Enjoy cleaner, healthier water on demand!
Some of the most popular water softener brands on the market today include:
- EcoWater
- Kenmore
- Fleck
- WaterBoss
- Autotrol
- GE
- Whirlpool
Don’t let the many options paralyze you. Instead, let us help you sort out your options.
Here’s what you need to know about each of these major brands:
EcoWater
EcoWater is a company based in Minneapolis, Minnesota. This location is important because it means all their parts are made in America. The same cannot be said for some other companies on this list. Many of them use lower-quality foreign-made parts in their softeners to save money.
In contrast, EcoWater’s American-made softeners are some of the most trustworthy and highest-quality models on the market. Their trustworthiness comes from the fact that they’re NSF/ANSI 44 certified. Products that receive this certification have undergone extensive testing to prove they do what they say they’ll do.
So, when you get an EcoWater softener, you can rest assured that it will soften your water. It will also remove radium 226/228 and barium to protect your health.
In addition, these systems have many high-quality features, including eco-friendly low salt usage and the ability to be monitored on your smartphone.
We frequently recommend EcoWater units to our customers for all these reasons and more. They may be more expensive than other options, but the extra investment is worth it for the long-term quality of results.
Kenmore
Kenmore was once a very popular water softener brand. However, its popularity has waned in recent years, and its parent company, Sears, declared bankruptcy in 2018.
Still, a Kenmore water softener system is a decent low-priced option for mid-sized homes. While it lacks the high-quality features of an EcoWater softener, it still gets the job done.
Plus, we at Angel Water served as the official Kenmore water softener service center in Chicagoland for many years. So, we have the expertise necessary to give a Kenmore system the maintenance it needs. We’d be happy to help you with your softener if you need it.
Fleck
Fleck has been around for over 40 years and is popular for its mid-priced water softeners. However, the issue with Fleck is that their softeners usually come with low-quality salt tanks.
This is because Fleck only designs the control valve on its tanks. Then, it’s up to the distributor to add the rest of the system. Unfortunately, many distributors use cheap foreign-made tanks and resin to save a few bucks.
Because of this, you should only purchase a Fleck water softener if you trust the company that makes it. Make sure the tanks and resin were made in America.
WaterBoss
WaterBoss units are some of the lowest-priced softeners on the market. As you might expect, the lower price means a lower-quality product.
WaterBoss softeners are notorious for decreasing the water pressure in a home. And while you save money on your initial purchase, it’ll probably cost you more money on service calls and replacement fees in the long run.
So, only purchase a WaterBoss if you need a quick and cheap fix.
Autotrol
The most significant benefit of an Autotrol water softener system is its metered control valve. This valve helps save money by keeping the system from using too much salt.
However, like Fleck, the control valve is the only thing Autotrol makes for its systems. It’s up to the distributor to add the rest of the parts to the unit, and some companies can use low-quality parts to do this.
So, if you buy an Autotrol softener, make sure you trust the distributor you’re buying from. One sign the distributor is trustworthy is if it’s willing to provide warranty coverage for the whole system rather than just the control valve.
GE
GE water softeners tend to be on the lower end of the price spectrum but come with many quality features. For example, many of the softeners allow you to adjust the water’s hardness level. The units can also learn to adjust to your home’s water-use patterns to ensure you always have enough soft water.
While these units seem nice, there are also some red flags to consider. One big one is that General Electric doesn’t make these softeners. Instead, the Chinese appliance company Haier makes them and pays to market them using the GE logo. Many of the units also only come with a one-year warranty. So, you may want to be wary of a GE softener if you’re looking for long-term coverage.
Whirlpool
Whirlpool is another affordable brand you will often find at big box stores. They provide various size options with different grain capacities depending on your needs. They also last between 10 and 15 years, making them dependable.
Whirlpool water softeners aren’t as trustworthy as top-quality NSF/ANSI 44-certified water softeners. However, they are an excellent option if you are on a budget and want a softener with a good reputation.
How to Find the Right Size Water Softeners
Your water softener must be big enough to consistently keep your household’s water soft. However, you shouldn’t just buy the water softener system with the highest grain capacity on the market.
Problems can occur when you install a system that is too small or too large for your home. When the system’s too small, you’ll frequently run out of soft water, and the softener will regenerate too often, leading to increased repair bills. Conversely, an oversized water softener won’t regenerate enough, which can lead to damage and bacteria growth in the resin tank over time.
Instead, you need to think like Goldilocks to find the right-sized system for your home. The system shouldn’t be too big or too small but just right. The softener that fits this bill is the one that can keep all the water your family uses soft while using the least amount of salt.
Follow the following steps to determine the right size for your home:
Step 1: Find Your Water Hardness
Start by finding out how hard your water is. There are several different ways to do this.
The most ideal way is to have the water in your home tested. An EPA-certified water test will reveal the exact number of grains per gallon you are dealing with. As a side benefit, the test can also detect any dangerous contaminants present, such as radium 226/228 or barium.
If you’d prefer not to get your water tested, you can also do some research to find out the average level of hardness in your region. The best way to find this information is by contacting your local water utility. Most city governments publish their annual water reports on the Internet. If it’s not online, you can also call to request a copy.
Finding your region’s hardness is not as ideal as getting your water tested because the hardness level of your water may differ from the reported total for the region. Still, it’s better to have an actual statistic to work with rather than a guess when determining the best water softeners in Chicago.
We should also mention that you can only get information from your local water utility if your home has city water. Homes with well water will need to test their water since water utilities do not regulate private wells.
Step 2: Calculate Your Water Usage
Once you know how many grains per gallon are in your water, you next need to determine how much water your household uses on average. Once again, there are a couple of different ways to do this.
The best way is to look at your monthly water bills. Each bill should say how much water your family consumed over the course of the month. Check those totals from the last few months to see how many gallons you consume per month on average. Once you have that total, you can then divide the number by four to approximate how many gallons you use per week.
If you can’t find how much water you use on average, you can estimate how much you use by doing some simple math. First, multiply the number of people in your home by the average amount of water one person uses per day, which is about 70 gallons. Then multiply that number by seven. This will give you an estimate of how many gallons your family uses per week.
Step 3: Find How Many Grains You Need to Soften per Week
Now that you know how hard your water is and how much you use per week, the next step is simple multiplication. Multiply the hardness of your water in grains per gallon by how many gallons of water you use per week. The resulting number is the number of grains your water softener will need to be able to remove each week.
Here’s an example of what this math will look like for a family of four with a water hardness level of 8 gpg:
- 4 people x 70 gallons per day = 280 gallons per day
- 280 gallons per day x 7 days = 1,960 gallons per week
- 19,600 gallons per week x 8 grains per gallon = 15,680 grains per week
The reason we’re calculating this total per week is that a softener should regenerate about once per week on average. So, the total is how many grains the softener will need to be able to remove before the regeneration cycle refreshes it.
Step 4: Determine a Water Softener’s True Grain Capacity
The final step is to find a water softener with the right grain capacity for your water usage. Unfortunately, this isn’t as simple as taking the grain capacity the softener’s manufacturer claims at face value. These numbers can be deceptive.
Most water softener systems will have a listed grain capacity of somewhere between 24,000 and 64,000 grains. The most common amount is 32,000 grains.
The problem with these listed grain capacities is they represent how many gallons the softener can handle in a controlled laboratory environment. Since the real world isn’t a controlled environment, the softeners never live up to this high bar. Instead, a 32,000-grain softener may only be able to handle around 27,000 grains before regeneration.
Furthermore, the system often requires an unrealistic amount of salt to handle its stated grain capacity. For example, a 32,000-grain softener will need around 18 pounds of salt per regeneration cycle. The cost of those salt bags will add up quickly!
So, rather than looking at a system’s grain capacity, which will require an unrealistic amount of salt, we recommend finding a system that can handle the number of grains you need with a manageable amount of salt. To determine this, find out how many grains per pound of salt a system can handle. The more grains per pound, the better.

Tips for Choosing the Best Water Softeners
So, you’ve narrowed your options down to a few different water softeners. Each system seems like it should be able to meet your family’s soft water needs, so now what? How do you identify the best choice from multiple options?
Once again, we’re here to help!
We’ve put together a list of the four most important factors to consider when making your final buying decision.
1. Favor NSF/ANSI 44 Certification
As we mentioned earlier, the best water softeners have NSF/ANSI 44 certification. This certification comes from the National Sanitation Foundation, which is a highly respected independent organization. They rigorously test and inspect water softeners and only give their stamp of approval to the best of the best.
So, what does purchasing an NSF/ANSI 44 certified water softener mean for you? The system is proven to work and will run more efficiently and be more reliable in the long run. As a result, you will save time and money and enjoy more peace of mind during the long lifespan of your system.
Therefore, if you’re looking at two different systems and only one has the NSF stamp of approval, we say go with that one!
2. Avoid Common Water Softeners Scams
Unfortunately, the water softener industry is fraught with scammers looking to rip you off. So, you need to be on your guard against scams.
Here are some red flags to watch out for to avoid buying a low-quality water softener:
- Not American-made – Water softeners produced outside America usually aren’t as trustworthy or durable as American-made systems.
- Only some parts have warranty coverage – The manufacturer and distributor should provide warranty coverage for the full system. If not, then it’s not a trustworthy softener.
- The Distributor has a bad reputation – Be sure to do your research on a company and factor its customer reviews into your purchasing decision.
- Salt-free water softener scams – Don’t trust a company that tells you a salt-free system will give you the same results as a salt-based one. It won’t.
Above all, only buy from a distributor and manufacturer you trust 100%. A water softener system is too big an investment to make an unconfident purchase.
3. Choose to Buy Rather Than Rent
When considering buying or renting, the main question you need to ask yourself is “Do I want short-term or long-term relief from hard water?” For most homeowners, we’re guessing the answer is long-term, as in multiple years of soft water.
If you’re in this boat, then buying is a vastly superior option to renting because you’ll save money on your softener in the long run. Renting will only be a cheaper option if you need the softener for a month or two. After that, those regular payments will start to add up. And even if your softener saves you money by preventing costly hard water problems, the rent payments will likely eat up those savings.
That’s why we almost always recommend buying a water softener over renting. It’s a worthwhile investment that will save you big for a long time.
4. Read a Lot of Customer Reviews
Don’t forget to look at customer reviews for the different softeners you’re considering. Read both positive and negative reviews for each system to get a good idea of its main strengths and weaknesses. These testimonials will help you gauge the integrity of the system and its manufacturer before you make your final decision.
The Importance of Professional Water Softener Installation
If you’re reading this section, we’re guessing you’ve purchased a water softener system or are about to. Congratulations! You’re well on your way to enjoying soft water throughout your home.
But don’t let your guard down just yet! There are still a couple of steps you need to follow to ensure you get the most out of your system.
The first step is to have your water softener professionally installed by a licensed plumber.
Why do we recommend having your system installed by a pro rather than installing it yourself? For one thing, many states legally require that a licensed plumber install all water treatment equipment. Such is the case in our home state of Illinois.
But beyond this, a licensed plumber will install your system the right way to get you all the benefits you’re looking for. Proper installation will also guarantee that your system will have complete warranty coverage. Many a warranty has been voided by one mistake in the installation process.
Of course, letting the professionals handle it will also save you from the time-consuming and stressful process of trying to handle it yourself. You will be able to sit back and relax as a licensed professional takes care of the grunt work to give you the soft water you deserve!
Water Softeners: Maintenance Best Practices
Once your softener’s up and running, you can keep it working well by ensuring it gets the regular maintenance it needs.
How much maintenance does a water softener need? The answer will vary from softener to softener depending on the manufacturer’s warranty requirements. Most companies require annual water softener service to maintain warranty coverage. Others will require inspection and cleaning twice a year. Whatever those requirements are, that’s how often you should service your system.
The good news is you don’t have to handle this maintenance on your own. A licensed plumber can also do this for you to meet all manufacturer requirements and keep your warranty coverage.
Of course, water softeners aren’t perfect. Even if your system receives regular maintenance, it still can have issues and require additional repairs.
Here are some signs your water softener may need service:
- There’s white crust around your faucets and shower heads
- The toilet bowl has a rusty ring around the water line
- Your skin has been feeling drier and itchier lately
- You’ve been having to replace salt more frequently than usual
- Your water has a slight brown, orange or grey tint to it
- The water pressure has decreased throughout your home
These are just some of the many symptoms of a softener in need of repair. The good news is a licensed technician can easily fix all of them! So, make sure to act right away if you notice them to get your system back in shape.
Water Softeners FAQs
What is hard water?
When water is referred to as ‘hard’, it simply means that it has a high level of dissolved minerals, especially positively charged calcium and magnesium ions. The presence of these highly charged mineral ions interferes with the ability of your water to act properly as a solvent. It causes soap to be less effective and it can coat the insides of your pipes and appliances causing low flow rates, high energy costs and ruined appliances.
What is water softening?
Water softening is a water treatment technique that removes calcium and magnesium ions from the water in your home or business. Through a process of ion exchange that utilizes a special negatively charged resin and a solution of sodium ions, a water softener is able to capture the calcium and magnesium ions before they are able to harm your plumbing system.
What are water softeners?
Water softeners are units that usually (but not always) consists of two tanks and a special valve assembly that coordinates the scrubbing of special, negatively charged resin with an ion rich sodium solution. A properly functioning water softener will remove excess calcium and magnesium ions before they are able to harm your plumbing system.
Why is water softening applied?
Water softening is used in households and businesses around the world to ensure high-quality water that can be used effectively for cleaning and won’t clog pipes or damage appliances.
Hard water causes limescale deposits which reduce the efficiency of water heaters and can increase the cost of domestic water heating by as much as fifteen to twenty percent.
Water softening can also extend the life of household appliances like laundry machines and dishwashers.
What do water softeners do?
Water softeners are a specific type of ion exchanger that are designed to remove calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions (often referred to as ‘hardness minerals’) from your family’s water.
Softeners are sometimes even applied to remove iron, though their efficacy for iron removal is considerably lower.
A water softener collects hardness minerals within its conditioning tank and from time to time flushes them away to drain. This flushing process is called regeneration and it’s a cycle that can be initiated manually, automatically at set intervals or even automatically based on the amount of water used. How your softener cycles depends on the type of control valve technology you invest in.
Softeners are rated on the amount of hardness they remove before regeneration is necessary.
How long do water softeners last?
A high-quality water softener with proper upkeep and maintenance can last several decades, however, many of the older units we see are not well maintained. People tend to forget about their water softening equipment until it breaks. They key to the longevity of your softener is proper salt levels, high-quality resin and reasonable annual service.
Which types of salt should I use?
There are three types of salt that are generally used for water softening:
- Rock salt
- Solar salt
- Evaporated salt
Rock salt has a water insolubility level of about 0.5-1.5%, which means it leaves behind some calcium sulphate that can eventually clog your system, but it’s less expensive than solar salt or evaporated salt.
Solar salt comes from evaporation of salt water and contains 85% sodium chloride. It has a water insolubility level of less than 0.03% and is generally sold in natural, chunky crystals or manufactured evenly formed pellets.
Evaporated salt is obtained from wet underground salt deposits that are harvested and dried. Evaporated salt contains between 99.6% and 99.99% sodium chloride and thus the cleanest (most water soluble) and most maintenance free salt you can use in your softener.
How often should one add salt to a softener?
The amount of salt used and how often you may need to add salt depends on a variety of factors including the number of people in your household, average water use, the size of your brine tank, and many more.
One of the most significant variables in determining how much salt you use is the type of control valve your softener uses to regenerate the system. Modern control valves can monitor your salt dosing needs to significantly reduce your costs and even notify you on your cell phone when it’s time to get more salt.
However, most softening systems will work just fine if you check them once a month and try to keep the brine tank at least half full.
How come water sometimes does not become softer when salt is added?
When you first install a new water softener, or sometimes, when you add salt to a system that has run out completely, the initial regeneration cycle may not significantly soften the water. This is because proper water softening requires a strong sodium ion solution. Immediately starting a regeneration cycle after adding salt doesn’t give the solution enough time to soak and dissolve the salt which can result in hard water getting past the softening system.
This is a temporary issue and should resolve itself with the next regeneration cycle, but if the problem persists, call us for an inspection to make sure everything is running properly.
How much do water softeners cost?
Newer water softeners are more efficient than older models and even among new models, the efficiency can vary significantly. These differences produce a variety of different price points.
The overall costs of water softening depend on the type of water softener, the initial hardness of the water and the amount of water used. When the water is very hard and used heavily, the costs of softening will rise.
Generally, the costs of water softeners are usually far outweighed by the benefits and cost savings obtained, through using softened water.
Do water utility companies and public systems provide softened water?
Although the opportunity to soften the water before it leaves a municipal treatment system certainly exists, it is not something that all utilities are required to do. Because hard water has a much more significant impact on hot water systems and municipal water mains are much wider than average residential plumbing, many municipal systems reduce costs by skipping this vital step in the water conditioning process.
Is softened water safe to drink?
Softened water is perfectly safe to drink. However, in areas with extremely high hardness, softened water might not be appropriate for preparing baby formula, and people on sodium-restricted diets should take into account the increased sodium that may be present in your drinking water and food as a result of extraordinary softening requirements.
How much sodium does one absorb from softened water?
Sodium intake due to softened water varies depending on the hardness of the water. On average, your sodium intake from drinking softened water is likely to be less than 3% of your recommended daily allowance.
The intake of sodium (Na+) from a home water softening process, is negligible compared to the total daily intake of many sodium-rich foods.
Will softening drinking water deprive it of essential minerals?
Softening will not deprive water of its essential minerals. Softening only removes ionized minerals that cause scale buildup and soap scum.
When does a softener resin need replacement?
In the hardest water areas resin may need to be replaced more frequently, but we’ve seen resin last as long as 20 years.
If you notice that your water is getting hard again (spots on dishes, itchy skin, dull hair and ineffective soap and detergents) The first thing to check is the brine reservoir or salt tank, as it is often called. Make sure there is salt in the tank before making a service call!
But if there is still salt and you don’t have softened water, the issue may be mechanical.
Does a softener brine tank need cleaning?
Generally speaking, it is not necessary to clean a brine tank; however, it is possible if the salt product being used has a high concentration of water-insoluble material. If there is a build-up of insoluble matter in the resin, the reservoir should be cleaned out to prevent softener malfunction.
Otherwise, only a serious malfunction or the introduction of foreign matter into the brine tank would necessitate its cleaning.
Can brine from water softeners damage a septic tank?
The Water Quality Association has performed studies on whether or not brine from softeners will damage a septic tank. These studies have indicated that a properly placed septic tank that works adequately in the first place cannot be damaged by brine that is discharged from a water softener. Softened water can sometimes actually help the longevity of a septic tank by reducing the amount of detergents discharged into it.
Can water softeners be used with lead pipes?
When naturally or artificially softened water ends up in lead pipe systems, it can cause the pickup of lead. Lead pipe systems have to be replaced before softened water can flow through them.
Can I take my water softeners with me when I move?
With modern water softeners, it is possible to take them from one installation location to another. Some modern systems even include quick-fit connections, similar to those used for laundry machines. If this is particularly important to you make sure to ask your Angel Water Expert for insight!
Ready to Find the Best Water Softeners for Your Home?
That’s the end of our water softener guide. Here’s a quick recap of what we covered:
A quality water softener removes hardness minerals like calcium and magnesium and impurities like radium 226/228 and barium from water. It also comes from a well-respected brand and a trustworthy manufacturer and has a high enough grain capacity for your needs. To get the most out of this softener, you need to have it professionally installed and annually serviced by a licensed plumber.
Got all that? We hope you did and found it helpful! But if you have any unanswered questions, we’d be happy to answer them for you. You can give us a call at 847-382-7800 to talk to an expert today! We proudly serve Long Grove, Kildeer and Hawthorne Heights from our primary location in Barrington, IL. Don’t forget we also have a second location in West Palm Beach, FL, to help with water-quality needs down there!
We’d also be happy to help you with any of your water softener needs. We can do everything from testing your water to professionally installing and maintaining our wide selection of NSF-certified systems.
Want Softer Water? Schedule an Appointment Now!
Find out how a water softener can help protect your home from hard water damage. Schedule an appointment with our water specialists today to explore the best solutions for your home.




