What is a Reverse Osmosis System? An Easy Guide for Beginners
This blog features the following key points:
• Reverse osmosis (RO) effectively removes up to 99% of dangerous contaminants from water.
• A reverse osmosis system contains several filters that make getting the cleanest possible water easy for you.
• The best RO system for your home will be NSF 58 certified, made in America and BPA-free.
• You can find affordable countertop, under-the-sink and whole house RO systems at Angel Water.

“But popularity can be deceptive,” you might say. “Do I really need a reverse osmosis system or not?”
We get it. You don’t have time to mess around with filters that don’t work. After all, your family’s health and well-being are at stake, not to mention your finances since these systems can be expensive.
Let us help you make sense of it all.
In this post, we’ll show you why an RO system is an excellent choice for making water healthier and safer for your family. Keep reading to have all the most important questions answered about reverse osmosis systems.
What is Reverse Osmosis Water?
Reverse osmosis is a simple process for removing harmful contaminants from water to make it much safer and healthier to drink. RO is such a popular filtration method because of the unparalleled amount of toxins it can remove.
What Does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
Some of our customers are skeptical. “Do reverse osmosis systems really work?” they ask incredulously.
Our answer is a simple confident yes, and the experts back us up!
The incredible reputation RO systems have for successfully filtering water isn’t just hype. Rather, according to the Center for Disease Control, RO is highly effective at removing all the following:
- Lead
- Hexavalent Chromium
- Sodium
- Copper
- Chloride
- Mercury
- Dangerous viruses like Hepatitis A and Norovirus
- Harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter
- Protozoa like Giardia and Cryptosporidium
- And more!
All the pollutants listed above have serious health risks associated with them. Reverse osmosis drastically lowers these dangers by massively reducing the amount of these scary substances that make it to your glass. The best residential RO systems can remove up to 99% of these contaminants from water. Few other filters can match this performance.
How Does the Science Behind RO Work?
You’re probably wondering how reverse osmosis is so effective. If you’re curious about the science behind this filtration process, we’ve got you covered with this simple overview.
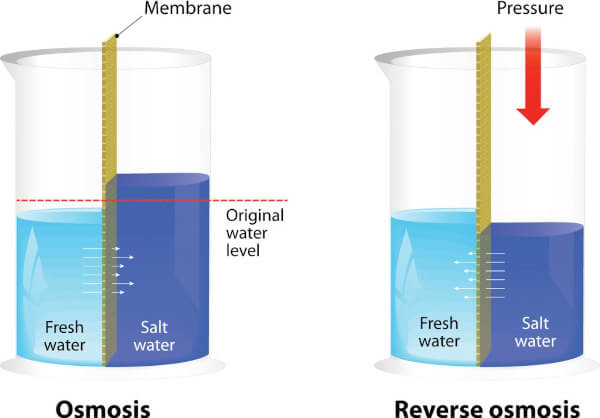
To understand reverse osmosis, you must first understand what osmosis is. Osmosis is a natural process water goes through when it encounters a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane is a barrier with holes small enough for water molecules to get through but not other types of molecules.
When water encounters this barrier, it tends to flow through it toward the side that has more particles and contaminants on it. The reason for this is water is adhesive, meaning it’s drawn to the objects it encounters and sticks to them.
The water will continue to flow through the membrane until the number of particles it contains on one side is directly proportional to the ratio of water to particles on the other side. In other words, the side of the membrane with less contaminants will have less water and the side with more will have more water. In this way, osmosis is all about balance.
The problem with this is we humans don’t want water to contain all these contaminants. We need the opposite to be true. That’s why we have technology to reverse the osmosis process!
Want more news from Angel Water delivered to your inbox?
Subscribe to our free email newsletter!
What Does Reverse Osmosis Do?
To make reverse osmosis happen, a system exerts pressure on water to force it through a semipermeable membrane in the opposite direction of where it would naturally go. Rather than flowing toward the side with all the contaminants on it, it flows away to the other side of the membrane. As a result, the water escapes to the other side, but all the pollutants it was carrying along with it get held back.
All the toxins we listed above can’t escape through the membrane because its holes are too small. The average pore size for a reverse osmosis membrane is approximately 0.0001 micron. (For some perspective, a micron is one twenty-five thousandth of an inch!) Only the water molecules are small enough to squeeze their way through such a tiny hole.
That’s why we love reverse osmosis for water filtration. The semipermeable membrane is so restrictive that the water is always much cleaner on the other side!
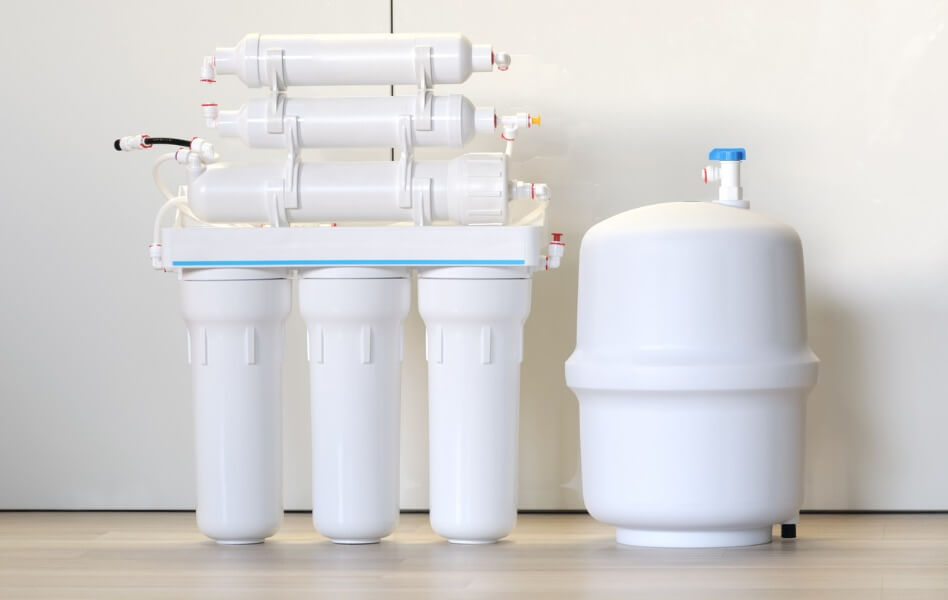
What is a Reverse Osmosis System?
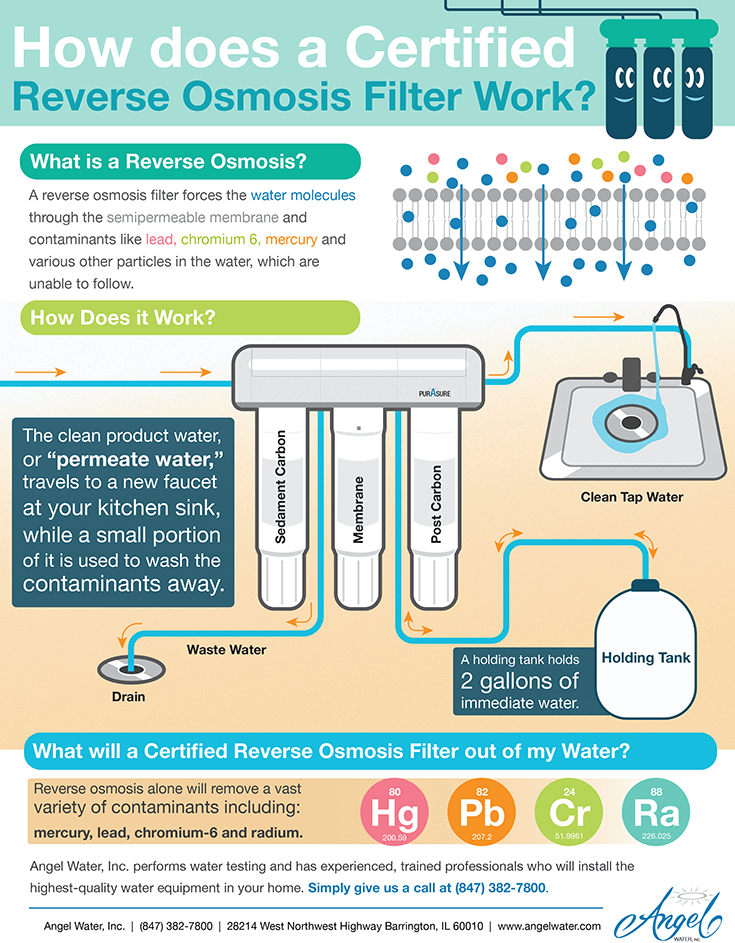
Now that you understand reverse osmosis, it’s easy to grasp how a reverse osmosis system works. An RO system is a device containing a semipermeable membrane for filtering water, which you can install in your home.
However, a semipermeable membrane isn’t the only filtration device RO systems use. Instead, every RO filter includes several other components, which help keep the water as clean and healthy as possible. These components include:
Unsure About Your Water Quality? Get a Free Water Test Today!
Contaminants can affect the safety and taste of your water. Get a free water test to check your water quality and see if a reverse osmosis system can help provide clean, pure drinking water.

- Sediment pre-filter
- Carbon pre-filter
- RO filter
- Carbon post-filter
- Additional polishing filters
- Water storage tank
- Faucet and pressure regulators
- Wastewater disposal system
Let’s take a closer look at what each of these components is and why all of them are important.
Sediment Pre-Filter
When water runs through a reverse osmosis system, it always goes through a sediment filter first. This filter removes any major chunks of dirt and debris from the water.
It’s essential to remove these larger particles from the water before it goes through the semipermeable membrane because the membrane is delicate. These large chunks could damage or clog the membrane if the sediment filter weren’t there to remove them.
Carbon Pre-Filter
The water also must go through a carbon filter before going through reverse osmosis. The carbon filter is essential for removing contaminants like chlorine and chloramine, which can damage the ultra-thin semipermeable membrane.
RO Filter
Once the pre-filtration process is complete, reverse osmosis filtration begins. The system pushes the water through the semipermeable membrane, which removes up to 99% of the dangerous contaminants we listed above.
Carbon Post-Filter
The water goes through another carbon filter after going through the RO filter to ensure it will taste great and won’t have any foul odors. This type of filter is also known as a polishing filter because it’s mainly concerned with the aesthetic qualities of the water.
Additional Polishing Filters
The best reverse osmosis systems come with additional filters for even higher water quality. For example, some come with an alkaline filter to improve the water’s pH level. Others have an additional VOC filter for removal of other potentially harmful organic compounds.
A common concern about reverse osmosis is that it also strips the water of minerals our body needs, such as calcium and magnesium. This is what some critics mean when they call RO water dead water. But the best systems add these essential minerals back into the water during the polishing stage to prevent this problem.
Water Storage Tank
Most RO systems come with some sort of tank to store the purified water. This storage receptacle is necessary because it ensures water will be available whenever you need it.
As you might imagine from the steps listed above, it takes a while for an RO system to fully purify the water. Without a storage tank to make the water available, you’d have to wait about five minutes for the water to come out once you turned on your faucet! Fortunately, the storage tank makes it possible to instantly pour yourself a glass of clean water!
Faucet and Pressure Regulators
Many RO systems also come with their own faucet and pressure regulators, which a licensed plumber can easily install in your kitchen sink. These stylish and convenient features make it easy to access the water whenever you want.
Wastewater Disposal System
Not all the water that goes through an RO system gets purified through the membrane. Some water gets left behind on the other side of the membrane with the contaminants. Most systems dispose of this water by funneling it through a tube, which leads to a drain. Newer, high-quality reverse osmosis system will waste one gallon in order to make one gallon of purified water. Old or Chinese systems can waste up to 20 gallons to make one gallon of water.
What is a Good Reverse Osmosis System for My Home?
If you’re convinced an RO system is right for your family, then the next logical question is, are all reverse osmosis systems the same? Good question!
The short answer is no.
A longer and more helpful answer is that many options are available, but the best reverse osmosis system for your home will check off the following boxes:
- NSF 58 certified for effective filtration
- 100% American-made
- BPA-free
The system will also be the right size for your home. RO systems typically come in three sizes: countertop, under-the-sink and whole house. Countertop systems are the smallest and easiest to install because they’re the size of a Keurig coffee maker, and you can plug them right into the wall. We often recommend countertop systems to people who live in apartments, high rise buildings or dorms, where plumbing installation isn’t allowed.
However, if you own your home and can have plumbing installation, an under-the-sink system might be a better option for you. As you may have guessed from the name, we typically install these systems under the kitchen sink, and they supply water through their own faucet. An under-the-sink system is better for larger families because it has a larger holding tank than the countertop system.
A whole house RO system is an excellent option if you need purified drinking water at multiple taps throughout your home. One of our licensed plumbers can easily install a reverse osmosis system like this in your basement next to the main water line.
Want to Start Getting RO Water Right Away?
We hope this guide has opened your eyes to what a reverse osmosis system is and what it can do for you. It will give your family the healthier, cleaner water you deserve so that you don’t have to keep wasting money on all those plastic water bottles.
Looking for an RO system that is easy to set up and inexpensive? We recommend the PurASure Countertop RO System. This system checks off all the boxes we discussed above, and you can plug it in on your counter and start getting clean water right away! Please click below to learn more about this powerful little filter.
Ready for Cleaner Water? Schedule an Appointment Now!
Ensure your family has access to clean, great-tasting water. Schedule an appointment with our specialists today to learn how a reverse osmosis system can purify your drinking water.



