What Do I Need to Know About Reverse Osmosis?

Learn the Key Information About RO Systems in One Comprehensive Guide
Do you know what reverse osmosis is? There are lots of different filtration techniques out there, including carbon, ion exchange, and ozone, but an RO system stands as the most efficient of them all.
In this guide, we’ll go over how reverse osmosis works, why it’s better than other filtration methods, how to choose a good system, and what kind of maintenance they require.
How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
First thing’s first: what is reverse osmosis, anyway? To understand how a reverse osmosis system works, first we need to understand diffusion, osmosis, and then reverse osmosis.
What Is Diffusion?
Before you can understand osmosis, first you need to understand diffusion.
This is the natural process where gasses and liquids tend to spread out evenly in a given space over time. When you release a gas into a room, like smoke, it doesn’t stay lingering around, but rather spreads out to evenly fill the room. Think of water as well—it’s evenly concentrated throughout. There aren’t chunks of denser water amid areas of less dense water.
The basic rule is that when there are two sections of a closed system with different concentrations of the same substance, the molecules will always tend to spread into the less concentrated section until there’s balance.
What Is Osmosis?
With an understanding of diffusion, we can move onto osmosis.
Again, imagine a closed system divided into two sections each filled with different concentrations of water and solute (any substance that’s dissolved in solvent to create a solution, like salt dissolving in water to create saltwater). The sections are divided by a semipermeable membrane, which is a barrier that lets some molecules through but not others.
Water molecules are much smaller than most solute molecules, so they’ll be able to move through the membrane. The solute molecules, because of their charges and because their size can block openings in the membrane, trap water molecules on their side. As a result, water accumulates on the side with the higher concentration of solutes instead of diffusing evenly.
Watch this video from Khan Academy for a visual demonstration of this process.
What Is Reverse Osmosis?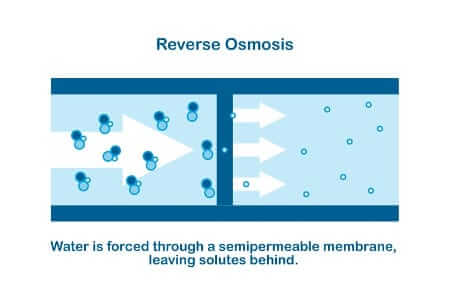
This may seem a bit self-explanatory, but reverse osmosis is the reversal of osmosis. What does that look like?
Think of the contaminants in your water as solutes. Naturally, when you move all the contaminants to one side of the water with a semipermeable membrane, the water flows to the side with the high-solute concentration. It stays with the contaminants, which is the opposite of what you want.
Want to get more helpful water information delivered to your inbox?
Sign up for our free email newsletter!
Reverse osmosis is when you apply lots of pressure and force the water back through the semipermeable membrane to the side with no solutes. The water molecules get pushed through the membrane, and the contaminants are trapped unable to follow.
Some of this purified water, called “permeate water,” is used to wash away those remaining solutes. The rest continues on to your fixtures and appliances.
For a more in-depth look at how reverse osmosis works, check out this previous post from Angel Water.
How Does Reverse Osmosis Compare to Other Filtration Methods?
So, how effective is reverse osmosis for filtering water, anyway? Let’s compare it against the other filtration media and methods on the market.
What Do Other Methods Remove?
For comparison, let’s go through some other types of water filtration systems and what they remove from your water.
- Carbon Filter: Many remove only chlorine. Others can remove mercury, lead, asbestos, and carcinogenic volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like those which boats leave behind in Lake Michigan. However, they can’t remove common inorganic contaminants including nitrates, chromium, arsenic, perchlorate, and fluoride.
- Ceramic Filter: Made from trillions of fossilized single-cell algae called diatoms, this filter’s microscopic pores filter out sediment but not chemical pollutants.
- Deionization Filter: This filter removes electrically charged molecules like mineral salts. It will not remove microorganisms like E. coli or non-ionic contaminants like VOCs and trihalomethanes.
- Distillation: This is the process of heating water up until it’s a vapor, then condensing the steam back into water. It removes minerals, microorganisms, and chemicals with a higher boiling point than water. However, it can’t remove chlorine, VOCs, or trihalomethanes.
- UV Systems and Ozone Systems: These systems can remove microorganisms, but not chemicals.
What Does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
You may notice that all of the above methods are unable to filter out significant groups of contaminants. This is a problem because you never know which of those is lurking in your water.
Here’s a list of what RO systems can remove:
- Fluoride
- Iron
- Zinc

Angel Water installs, services, and repairs reverse osmosis systems like this one from EcoWater. - Mercury
- Selenium
- Phosphate
- Lead
- Arsenic
- Nickel
- Manganese
- Cadmium
- Cyanide
- Chloride
- Chromium-6
- Nitrates
- Perchlorate
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Bacteria like cryptosporidium
Additionally, most RO systems also include an activated carbon filter to pick up chlorine, trihalomethanes, and VOCs. Together, these components form a complete filtration system that provides the highest-quality drinking water.
For a more detailed comparison of what these filtration methods do and don’t remove, see this post we made on the topic.
How Do I Choose the Right RO System?
Of course, not all systems are created equal. The market is full of makes and models that vary widely in price and quality. So, how do you choose?
The most important thing to look for is NSF certification. NSF International was formerly called the National Sanitation Foundation. They’re a widely respected independent organization that verifies manufacturer claims and develops industry standards for many different products. Look for an RO system that’s NSF-certified, because this that means the product has gone through rigorous testing to prove that it really works the way it’s supposed to.
Don’t just glance at the “NSF-certified” seal, though. Look at what it’s certified for. How many gallons is it certified to filter before needing a replacement filter? A shady company might proudly display the NSF certification seal in its marketing materials but not mention that it’s only certified to work for 25 refills. Pay close attention and make sure your RO system will fit your needs.
If you’re looking for a more comprehensive guide to choosing the right water filtration system, try this one from Angel Water.
How Do I Maintain My RO System?
Like any other piece of equipment, a reverse osmosis system will require some maintenance to keep it running in top shape year after year. Each stage of the filtration system requires its own attention. Here’s a breakdown of what to expect for each of those stages.
- Sediment filter—This stage of the RO system removes visible sediment, including dust, gravel, and salt. This filter needs to be changed every 6 months.
- Membrane—The semi-permeable membrane removes 95% of total soluble solids and heavy metals, including arsenic, copper, and lead, as well as microorganisms like giardia and cryptosporidium. It needs to be changed every 2-5 years.
- Carbon filters—The water goes through a carbon filter as it’s leaving the RO storage tank. This polishes the water and removes unwanted tastes and odors. You should change it every 6 months.
- Calcite Filter—The final stage is the calcite filter. Since the water has been stripped of solids, this filter adds minerals back in and infuses the water with electrolytes. This creates ideal drinking water. The filter should be changed every 2-5 years.
To read further about maintaining your RO system, see this previous Angel Water post.
Secure a High-Quality RO System from the Pros at Angel Water
If you’re looking for the highest-quality water, you should invest in reverse osmosis. If you want the highest-quality RO system, you should turn to the professionals at Angel Water. We’ve been the leading experts on reverse osmosis in Barrington, IL and the Chicago area for decades, deliver the best value around. We supply, install, and service high-quality NSF-certified reverse osmosis systems, and our technicians have years of hands-on experience. Give Angel Water a call at (847) 382-7800 and we’ll answer all your water treatment questions.
Interested in a Water Softener System for Your Home?
You don’t have to live with a dry, itchy scalp and brittle hair anymore! It would be our pleasure to help you find the right water softener to make your showers enjoyable again.
Please give us a call at (847) 382-7800 or visit our water softener page to learn more.



